What is Generative Engine Optimization?

Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Marketers Can’t Ignore Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in 2025:
User Trust in AI:
According to Search Engine Land, 70% of consumers already trust generative AI results, and 79% will use AI-enhanced search within the year.
Traffic Redistribution:
As generative engines satisfy queries instantly (e.g., Google’s AI Overview, ChatGPT’s summaries), * According to the Ahrefs report, clicks to websites for informational queries have dropped 34.5%*.
Competitive Surge:
A report says that early GEO adopters see up to 40% higher visibility in AI responses by tactics like citing sources, adding statistics, and quoting experts.
GEO isn’t replacing SEO, it’s evolving and improving on it. Where SEO targets keywords for ranking, GEO targets AI synthesis, demanding content that’s credible, structured, and context-rich. Ignoring this shift means vanishing from the next frontier of search.

What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Wondering what this whole Generative Engine Optimization thing is about? Let me break it down for you.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the next frontier of content strategy, where success isn’t just measured by how well you rank on Google, but by how often AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews cite your content in their responses. More people are turning to AI for answers every day—and with that shift, AI citations are becoming a new source of digital trust. When AI tools quote your website, it signals credibility to users, reinforcing your authority and boosting brand recognition in the moments that matter most.
GEO helps ensure that your content is part of what AI surfaces, not just buried in traditional links. At its core, GEO is about understanding how AI interprets, prioritizes, and delivers content and tailoring yours to be favored in that process.
What makes GEO different?
While traditional SEO is about climbing search rankings, GEO is about becoming the source, making your content so clear, trustworthy, and data-rich that AI-powered search engines include it in their response, without hesitation. Think of it as SEO’s smarter, more dynamic sibling. Instead of just optimizing for keywords and backlinks, GEO focuses on how AI models interpret context, purpose, and credibility. It’s not just about being found; it’s about being cited, quoted, and recommended by the Generative AI platforms.
📈 Why It Matters:
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) isn’t just another content trend—it’s a measurable performance upgrade. GEO-optimized pages have been shown to receive up to 40% more visibility in AI-generated responses compared to standard SEO-driven content. That visibility boost translates into greater brand exposure, more clicks, and stronger authority in a world where AI is often the first source users engage with.
Bottom line: If your content isn’t GEO-optimized, you’re missing out on a rapidly growing stream of high-quality traffic. In an AI-first search environment, GEO turns ordinary content into high-performing assets by increasing visibility, trust, and engagement. And it’s not just about impressions; leads from AI-generated recommendations have been shown to convert up to 4.4x better than those from traditional search. That’s because when users see your brand cited by an AI system they trust. It carries the weight of a neutral, authoritative endorsement. In short: building for GEO isn’t optional anymore, it’s a competitive edge.

Vishvak Murahari∗
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
murahari@cs.princeton.edu
Pranjal Aggarwal
Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
New Delhi, India
pranjal2041@gmail.com
Tanmay Rajpurohit
Independent
Seattle, USA
tanmay.rajpurohit@gmail.com
Ashwin Kalyan
Independent
Seattle, USA
asaavashwin@gmail.com
Karthik Narasimhan
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
karthikn@princeton.edu
Ameet Deshpande
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
asd@princeton.edu
How Generative Engines Work
Generative engines like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overview, and Perplexity combine real-time web search with the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Instead of serving up links, they generate direct, conversational answers by blending fresh data with deep knowledge from their training sets. This hybrid approach allows for responses that are more natural, informative, and up-to-date than traditional search results.
LLMs are trained on massive datasets, web pages, books, forums, and code, and can generate answers even offline. But modern AI engines enhance this by pulling real-time insights from the web, improving relevance and accuracy. For example, Perplexity cites live sources alongside answers, while Google’s AI Overview weaves summaries directly into search results.
In short, generative engines are part search engine, part AI assistant offering direct, contextual answers rather than just a list of links which you would have to visit to get the answer. This is why Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is essential: it ensures your content is visible, trusted, and cited by AI when users search with a particular intent.
GEO vs SEO (2025 Hottest Battle)
| Aspect | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank higher in traditional search engine result pages (SERPs) | Be cited and featured in AI‑generated summaries (ChatGPT, Google AI Overview, Perplexity AI) |
| Target Engines | Google, Bing, Yahoo | Generative engines: Google AI overview, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Bing AI |
| Content Focus | Keyword-rich content, backlinks, and on-page optimization | Context-rich, structured, AI‑readable content that machines can understand and cite |
| Technical Strategies | Meta tags, sitemaps, crawlability, URL structure | Schema, conversational Q&A formatting, [llms].txt, AI‑crawlable structures |
| Measurement Metrics | Rankings, organic traffic, click-through rate (CTR) | Citation frequency in AI answers, presence in summaries, and AI‑driven referral traffic |
| Optimization Tools | SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, Google Search Console | AI‑specific tools: AI Monitor, BrandRank.ai, Otterly.ai—tracking mentions and sentiment in generative engines |
| Typical Outcome | More clicks, higher page views, improved SERP visibility | Direct answer inclusion, zero‑click content display, and increased brand visibility within AI responses |
🚀 Key Impacts of GEO on Digital Marketing
| Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Search Visibility | Instead of ranking #1 on Google, GEO helps your content appear directly in AI-generated answers and summaries. |
| Traffic Sources | More traffic now comes from AI-driven referrals (e.g., Perplexity citations, Google AI source links) than traditional search clicks in many niches. |
| Brand Authority | Being cited by LLMs positions your brand as a trustworthy expert in your domain, similar to getting quoted by the media. |
| Content Strategy | Forces a shift from keyword stuffing to context-rich, AI-readable content designed for understanding, not just ranking. |
| Competitive Edge | Early GEO adopters are gaining ground in emerging search channels while others are still focused solely on outdated SEO tactics. |
Challenges Marketers Face While Doing Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
While GEO opens the door to future-ready visibility, it’s not without serious hurdles. Marketers who’ve mastered traditional SEO are discovering that GEO plays by different rules, often hidden beneath the surface of generative engines like ChatGPT, Google AI Overview, and Perplexity.
Let’s explore the most common (and critical) challenges marketers face:
⚠️ 1. Lack of Transparency in Generative Algorithms
Unlike Google’s search algorithm which, though complex, operates with well-documented ranking signals, LLMs function more like black boxes. Their internal reasoning is opaque, making it difficult to understand exactly why certain responses surface or why specific sources are cited. It is hard to pinpoint:
- What sources and content do they prioritize?
- How do they decide what to cite?
- Why is certain content surfaced while others are ignored?
- What sources and content do they prioritize?
🧩 Solution: Structure your content with clarity and semantic relevance, and monitor AI tools like Perplexity to see what is actually being cited.
📉 2. Decline in Traditional Traffic
With AI providing instant answers, most people don’t bother jumping to a full web page anymore. This creates:
- Zero-click experiences = fewer website visits
- Traffic numbers that drop overnight, even when you still hold the top spot.
- Zero-click experiences = fewer website visits
🚧 Solution: Shift your attention from just tracking page views to actively measuring brand visibility and citation presence in AI-generated answers. It’s not just about being seen—it’s about being mentioned. In the age of conversational AI, visibility within answers equals influence.
🔄 3. Constantly Evolving AI Models
Generative engines are still in their early stages and evolving rapidly. As these technologies continue to learn and adapt, the strategies for gaining content visibility are shifting just as quickly, often faster. What earns your content a citation or visibility this week might be entirely overlooked the next.
- Since the online world is constantly moving, you can’t expect your content to stay in the same spot.
- To stay relevant, it’s crucial to monitor changes closely and continuously.
🛠 Solution: GEO is not a one-time task. Stay flexible with your plan, spot new trends fast, and refresh your pieces before they go stale.
🗃 4. Content Structure & Format Limitations
A lot of marketers still rely on traditional formats: long blogs, sales landing pages, or keyword-heavy SEO posts. The problem is, those styles often don’t match what AI- powered search engines really value in the content. They look for:
- Clear, concise answers
- Structured formats (FAQs, Metadata tags, schema code, and .txt-style notes)
- Schema and [llms].txt-style visibility
- Clear, concise answers
💡 Solution: Rethink formatting for machine readability and semantic clarity.
📊 5. No Established Benchmarks or Analytics
Unlike SEO (with tools like Google Analytics, GSC, Ahrefs), GEO is still in its early stages. Marketers struggle with:
- Knowing how well their GEO content is performing
- Measuring AI citations or generative visibility
🧪 Solution: Use emerging GEO tools like AI Monitor, Otterly.AI, or BrandRank.ai. They can help you spot mentions, keep tabs on citations, and gauge overall sentiment across platforms that use generative tech. To go through a detailed list of GEO tools, and learn more about their pros and cons, you can visit our blog: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Tools
Proven Techniques to Boost Visibility in AI-Powered Search
To stand out in AI-powered search, you need more than traditional SEO—it’s about crafting content that AI finds credible, relevant, and reference-worthy. These proven techniques focus on enhancing your brand’s chances of being cited directly in AI-generated answers, where trust and context matter more than ever. Some of the strategies that we would vouch for are:
1. Optimize AI-Bot Crawlability
Ensure AI crawlers (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini) can access and understand your site.
Key actions:
- Do not disallow crawlers in the robots.txt file
- Fast load times + mobile optimization
- Fix crawl errors (e.g., broken links)
- 63% of websites fail core crawlability criteria.
2. Strengthen Reviews on Platform Ecosystems
AI models prioritize reviews from trusted platforms.
Key actions:
- Try to increase authentic reviews on platforms like Yelp, G2, or niche platforms
- Focus on products/services with detailed feedback
- Keep an eye on the reviews and respond when needed to stay credible.
3. Join Niche Communities (e.g., Reddit)
Generative engines value authentic community discussions.
Key actions:
- Pick the right subreddit or forum, share helpful tips, and skip the hard sell so you don’t come off like spam.
- Foster discussions about your brand/products
- Encourage upvotes and shares to boost visibility
4. Build Credibility with Citations and Credible Content
AI favors trusted, well-sourced content.
Key actions:
- Cite reputable sources (studies, expert journals, or articles from authors who are well-known in your field).
- Include expert quotes/contributions
- Publish original research or in-depth analysis
5. Expand Contextual Relevance via Semantic Keywords
Optimize for natural language queries, not just keywords.
Key actions:
- Target long-tail, conversational phrases
- Group-related terms (semantic clusters)
- Cover topics comprehensively (“topic clusters”)
6. Leverage Traditional PR & Branding
Offline visibility fuels AI training data.
Key actions:
- Secure press coverage in industry publications
- Publish thought leadership (e.g., whitepapers, webinars)
- Boost brand mentions across credible sites
For a deeper dive into the techniques that would help you out with Generative Engine Optimization, check out the full article: 👉 Top 11 Generative Engine Optimization Techniques – AI Monitor
🧰 Tools That Enhance the Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Process
Your essential toolkit for winning in AI-powered search
As AI-generated answers become the new front door to the internet, GEO is changing how brands appear in tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and more. But executing a strong GEO strategy requires more than just great content, it requires the right tools.
Here’s a curated list of powerful GEO tools shaping the future of AI visibility in 2025:
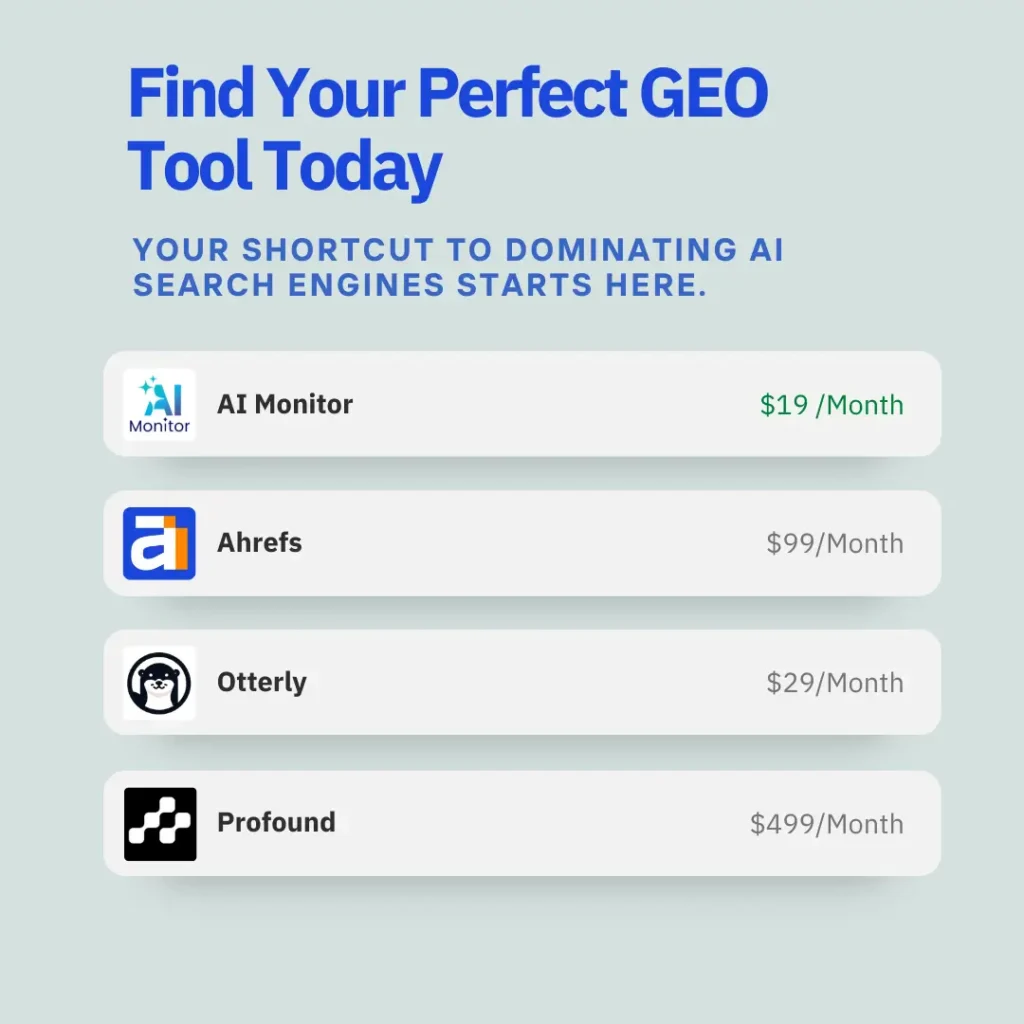
AI Monitor offers real-time tracking of your brand’s visibility in AI search platforms such as Google’s AI Overview, ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity.
It monitors prompts, sentiment, citations, and competitive keyword coverage, making it the most complete and useful GEO platform on the market.
✅ Used by top agencies to drive 500%+ visibility gains.
Semrush rolled out GEO-friendly tweaks like prompt tracking and AI-answer detection. It’s a smooth way for traditional SEO professionals to integrate GEO without rebuilding their stack.
💡Starter plans kick off at $99/month.
Otterly.AI is an affordable tool that provides basic prompt visibility and keyword-to-prompt matching.
It’s easy to use and offers fast setup, though results can be inconsistent.
💸 If you’re in the early stages of testing geo-targeted campaigns, this approach pays off.
Profound delivers high-end AI behavior mapping, brand risk forecasting, and prompt-level insights for large organizations.
If you need deep analysis and long-term strategy planning, this is your tool.
📊 Requires premium licensing and advanced onboarding.
BrandRank.ai offers a hybrid approach: AI monitoring paired with human review to detect brand misrepresentation or legal risk in generative answers.
🔒 Especially valuable for finance, healthcare, or government orgs.
Ziptie.dev is a developer-first API toolkit for tracking generative engines at a technical level.
You can build your dashboards, alerts, and pipelines to follow brand, product, or keyword prompts as they evolve.
⚙️ Ideal for custom solutions and AI research.
Did you know there are over 50+ GEO tools already shaping the future of AI-driven search?
We’ve put together a curated list of the most powerful Generative Engine Optimization tools on the planet, your one-stop resource to stay ahead in the game.
Got a GEO tool we haven’t included yet? Drop us an email, and we’ll make sure it gets the spotlight it deserves
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Pros vs. Cons
| Aspect | Pros (Advantages) | Cons (Challenges) |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | ▶️ Appears in AI-generated answers (e.g., Google SGE, Perplexity), capturing users before they click links. | ▶️ Traffic cannibalization: Fewer clicks to websites if the answer fully satisfies users in the AI snippet. |
| Authority Building | ▶️ Source attribution (e.g., "According to [Your Site]") boosts brand trust and E-E-A-T. | ▶️ Zero control over how generative engines summarize/represent your content. |
| Content Strategy | ▶️ Rewards comprehensive, well-structured content (not keyword stuffing). | ▶️ Requires significant content restructuring: Depth > brevity, multi-perspective coverage. |
| Future-Proofing | ▶️ Prepares for AI-dominated search (25–60% of queries may use generative results by 2026). | ▶️ Rapidly evolving landscape: GEO tactics may become obsolete quickly as AI models update. |
| ROI & Traffic | ▶️ High value for complex, research-driven queries (e.g., comparisons, guides). | ▶️ Unclear monetization: Harder to track conversions if users stay in the AI interface. |
| Technical Execution | ▶️ Less reliance on backlinks vs. traditional SEO. Focuses on content quality. | ▶️ Opaque ranking signals: Lack of clear guidelines (vs. Google's SEO standards). |
| Competition | ▶️ Early-mover advantage: Fewer sites actively optimize for GEO. | ▶️ Dominated by established authorities (e.g., governments, universities, major publishers). |
| User Experience | ▶️ Drives content toward user intent and problem-solving. | ▶️ Forces creators to prioritize AI readability over human engagement (e.g., emotional hooks). |

Do You Know What ChatGPT is Saying about Your Brand?
Don’t wait for a crisis. Proactively manage your brand’s reputation in the age of AI. To learn what AI is saying about you, book 1:1 Meeting with the #1 GEO Expert in the world.
📚 How You can Learn Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
As AI-driven search transforms how content is discovered, learning Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) isn’t just optional, it’s essential for marketers, creators, and SEO professionals who wish to stay ahead of the curve.
But where do you start?
That’s exactly why we’ve created a free, in-depth course—designed to take you from GEO beginner to expert, even if you’re not technically inclined or deeply familiar with how AI works. It breaks down complex concepts into practical, actionable steps to help you succeed in the AI-powered search landscape.
🎓 What You'll Learn:
- How AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity source and surface content
- What makes content “AI-citable” in zero-click summaries
- The tools, techniques, and frameworks that top brands use to rank in generative answers
- Real-world case studies and prompt-based visibility strategies
Whether you’re in SEO, content marketing, or digital strategy, this course will give you the GEO fundamentals and advanced tactics to thrive in the AI-first web.
👉 Start learning here (free):
https://getaimonitor.com/best-generative-engine-optimization-geo-course-for-free/
🔮 Our Prediction on GEO
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is no longer a futuristic concept, it’s the foundation of digital visibility in an AI-first search ecosystem. With platforms like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Perplexity providing direct answers before users even click a link. Brands that fail to adapt risk becoming invisible. Just as businesses that ignored the SEO bandwagon in the early 2000s faded from traditional search, those overlooking GEO today will be left behind in AI-generated results.
By 2026, we expect 40–60% of all discovery traffic to come from generative engines, not traditional SERPs. Prompts will replace keywords, and earning citations from AI models will become the new gold standard of authority. It won’t be about ranking on page one, it’ll be about being the trusted source AI draws from.
Real-time monitoring, prompt-aware content, and semantic depth are the building blocks of tomorrow’s digital strategy. GEO isn’t a trend, it’s the next era of search. The brands that act now will shape it. The ones that don’t? They’ll be searching for relevance in a landscape that’s already moved on.